Bibliography
"Geothermal
Energy." RE News RSS. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Jan. 2013. <http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/tech/geothermal-energy>.
"How Geothermal Energy
Works." Union of Concerned Scientists. N.p., 16 Dec. 2009.
Web. 20 Jan. 2013.
<http://www.ucsusa.org/clean_energy/our-energy-choices/renewable-energy/how-geothermal-energy-works.html>.
"Benefits of Geothermal Energy." National
Geothermal Collaborative, n.d. Web.
"Geothermal Energy Advantages And
Disadvantages." Energy
for Mankindorg RSS. N.p., 2011. Web. 19 Jan. 2013.
D. Swain. Disadvantages
on Geothermal Energy. 28 de
Jun de 2007.
<http://voices.yahoo.com/five-disadvantages-geothermal-energy-407841.html?cat=15>.
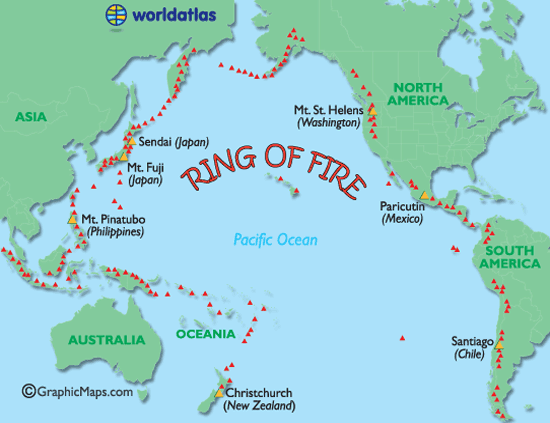
"Ring of Fire Map - Major World Volcanoes, Active World Volcanos Map - World Atlas."Ring of FireMap - Major World Volcanoes, Active World Volcanos Map - World Atlas. N.p., n.d. Web. 27 Jan. 2013.